| Added | Tue, 29/11/2016 |
| Источники |
Some of the important material evidence of the NOF received from the eyewitness, in addition to the description are the photos. Therefore, to find the causes depicted in the picture of the phenomenon the researcher is very important not only to understand the physics of possible explanations, but to be able to match it with the conditions in which this photo was taken. Most often, the researcher necessary information about the light, time of day, the use of software for photo montage, etc.
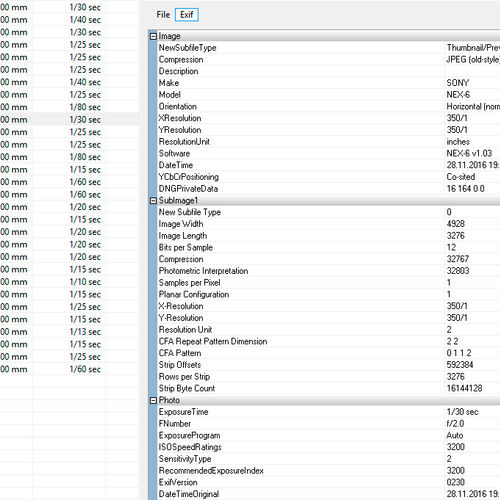
In photos taken with digital cameras, such information is in the EXIF. Exchangeable Image File Format is a standard that allows to add images and other media files with additional information (metadata), commenting on this file, describing the conditions and methods of its production, authorship, etc. to See EXIF of pictures from almost any program for viewing images.
Consider the researcher is interested in the basic settings:
- excerpt
- aperture
- ISO
- using the flash
- the resolution of the frame
- focal length
- the size of the matrix
- type white balance
May also be interested in the date and time of shooting, geographic coordinates and the address of the place of shooting, camera manufacturer and model. These data are most often reported by the witness, but the contents of the EXIF can be used as a refiner.
Let us examine in more detail what kind of information gives the researcher each parameter.
Exposure. This is the time interval during which light exposes the plot of a photosensitive material or a photosensitive matrix.
Retreats modern cameras use a standard scale of shutter speeds in fractions of a second (1/2, 1/8000), as well as in seconds (1, 2), etc. the shorter the shutter speed, the less exposure at a fixed relative aperture (and the darker the image). Aging affects the fixation of moving objects. Short excerpts (usually shorter than 1/500) clearly record object, and long exposures (usually more than 1/30) allow to achieve the effect of "apparent motion", in which the object is becoming blurred bands (the track). The exposure time and the long track facility allows the researcher to estimate the speed of the object in the frame. Also the track could be mistaken for something unexplained (for example, a UFO or a Ghost, depending on the location of a moving object).
In modern photographic technique is most often used aperture shutter, and the light begins and ceases simultaneously over the entire image field, which allows it to be exhibited at the same time. When using focal focal-plane shutter or shutter, exposure occurs by means of a moving slit, which in some cases is much less than the size of the entire frame, so the light on different pixels of the image falls at different periods of time. This can lead to the effect of the temporary parallax, which manifests itself in the distortion of the shape of fast moving objects.
Aperture. This is a divider, allowing to adjust the lens aperture by changing the diameter passing therethrough beams of light. The camera's aperture setting determines the depth of field of the image, i.e. the higher the value, the more objects in the frame will be in focus. In addition to adjusting exposure and depth of field, the change in relative aperture with aperture affect other important parameters such as diffraction (the phenomenon that manifests itself as a deviation from the laws of geometric optics with the propagation of waves), aberration (error or error image in the optical system caused by deviation of the beam from the direction in which he would have to go in a perfect optical system) and vignetting (the smaller the hole, the less light fall-off from center to edges of the image). The hole shape of the aperture also affects the shape of objects blur (bokeh), which is often taken by the witness during a UFO or mystical entity.
ISO. The dependence of the numerical parameters of the digital image from the exposure received by a photosensitive matrix. Thus, the ISO determines how sensitive the camera is to light. Thus, the greater the value of this parameter, the more "noise" in the photo.
For Sunny and cloudy weather optimally use ISO 100 or 200, with a strong cloud - to 400, and in a room up to 800 or higher (depending on shooting conditions).
The use of flash. The flash is an artificial light source designed to generate short light flashes of high intensity. This option, in particular, says the researcher about why the pictures of the things harsh shadows, objects in the foreground much lighting up, etc. the Flash can highlight and distort objects, hardly noticeable under normal lighting conditions (e.g., dust), giving unusual shadows or reflections (e.g. on glass), which is often mistaken for supernatural phenomena (orbs, ghosts, UFOs, etc.)
The resolution of the frame. A value defining the number of points (elements of the bitmap) per unit area.
Focal length. Physical characteristics, depending on the design of the lens. The longer it takes, the farther from the rear plane of the lens a sharp image of an object placed in front of the lens.
Lenses designed for shooting objects of large size with small distances (e.g., architectural and interior photography), must be wide, i.e. the focal length of the lenses is much smaller than the diagonal of the frame, and the angle of the image more than the normal lenses. They give large perspective distortion, change the shape of the objects located at the edge region appear to have greater vignetting on the edges and corners of the frame.
Lenses designed for shooting distant objects close-up should have a large focal length, hence a small angle of view. Telephoto lenses, or longer lenses, have not less than 1.5 times larger diagonal of the frame, the less depth of field and to a lesser extent, convey the breadth and depth spaces, “flattening” the image, i.e. visually unite the far and forward plans.
The size of the matrix. The matrix camera consists of sensor pixels. The more, the higher image detail.
Type white balance. White balance is a setting method of transferring a color image, which determines the compliance of colors of the image of object colours of a subject. In many digital cameras in the menu you can manually set the lighting type of the frame: the sun, daylight, blue (shadow) and a cloudy sky, fluorescent, incandescent, flash, etc. - and the camera makes an adjustment for the appropriate color temperature. Incorrect white balance can quite distort the colors in an image, "transforming the" familiar things in the mystical.
The combination of the above parameters gives a complete picture of the shooting conditions and allows you to build educated guesses about the origin of the objects in the pictures.
Of course, such information should not be trusted, since there are programs that allow you to edit, and partially or fully remove EXIF-image recording.
Translated by «Yandex.Translator»
Log in or register to post comments
