| Added | Fri, 19/01/2018 |
| Источники | журнал "Наука и жизнь". статья "Я запускал в небо НЛО". Признания ветерана ЦРУ"
|
| Версии |
One of the waves of mass UFO reports came in 1947. Many witnesses claimed to have seen in the sky large glowing ball. Such observations are characteristic not only of the witnesses with land, but are found in the reports of the pilots (including the military).
For example, in one of the books about UFOs described such a case of observation of an unidentified flying object:
Night of the highway in the sky appeared a floating red lights. They shifted to the field side and fell to the ground. You can see the object three-story-tall building, over which came the other lights, sometimes descending to the main subject.
Witnesses also described just bright stars that hung in one place for a long time (unlike ordinary stars, which were moving due to the rotation of the Earth), or bright light flashes in the sky (seen them over the United States mostly in the 50-60-ies of XX century).
Such repeated observations of the same type of UFO may be associated with the increasing trend in this period, the launches of reconnaissance balloons.
This article supplements the information provided in the article the History of Aeronautics, aviation and space exploration.
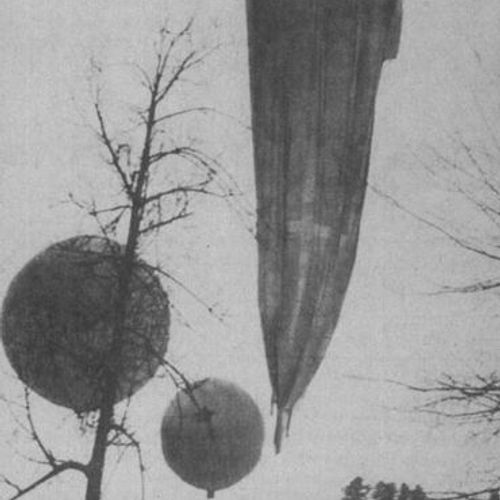
High-altitude balloons (aka "stratosphere" or "stratospheric balloons") is an unmanned balloon, usually filled with helium or hydrogen and a rare methane that go into the stratosphere, generally reaching heights of 18 to 37 thousand feet. Although the stratosphere, in fact, is a balloon, the device has a number of significant differences in the power of flight conditions. The density of the air in the lower stratosphere is an order of magnitude less and at altitudes of about 30 km 2 orders of magnitude less than at sea level, so to create a sufficient static lifting force of the volume of the container should be large enough (of 14 000 m3 to 850 000 m3 by the largest cylinder). Since the height of the gas expands, the cylinder changes its shape from elongated pear-shaped (at the start) to spherical (near the top point of the flight). The shell for such balloons are made from a very thin and durable plastic (usually made from shiny reflective plastic to prevent overheating of the ball, which, thanks to the backlight of the Sun, greatly distinguished him in the sky) . Now the cylinder is usually equipped with a valve to bleed gas, which is used to ensure the lower stratosphere and reduce the speed of ascent during take-off. Gondola with equipment or people often had external lighting parts – bright red lamps. Sometimes used "managed" balloons, which used to maneuver through the air flow (change of direction of flight by changing the height of the ball, making it in turn fell into multidirectional air flow).
The first hydrogen balloon was launched in France in 1783, Professor of physics, Jacques Charles and the famous designers brothers Robert.
The world's first stratospheric balloon was designed and built by the Swiss scientist Auguste Piccard. May 27, 1931 he, together with Paul Kipferon made the first ever flight into the stratosphere from Augsburg, Germany, reaching a height 15785 M.
Flying high-altitude balloons were connected many military projects around the world. Many of them, because of their secrecy at the time, was mistaken for unidentified flying objects, which are not only observed from the ground and aircraft, but has fueled speculation about the attack of UFOs on aircraft, separation from the main ship a whole Armada of UFOs (project "Grab Bag"), and concealing the military remains of UFOs, wrecked ("theRoswell incidentand project Mogul"). Here are the most notable projects that have used the balloons from declassified today.
Project Mogul
Project Mogul (sometimes referred to as "operation Mogul) was a top secret project of the Military-air forces of the USA, associated with the use of microphones for flying on high altitude balloons, whose main purpose consisted in detection at long range of the sound waves from the Soviet Union tests atomic bombs. This project was carried out from 1947 to beginning of 1949. The project used a lot of balloons, carrying a platform with microphones and radio transmitters to relay signals to earth. The first bottles for "Mogul" consisted of a large number of latex weather balloon, but soon they were replaced by huge plastic balloons made of polyethylene. Also the pressure transducers, according to testimony which was produced ballast that was necessary to maintain a constant height.
Skyhook balloon
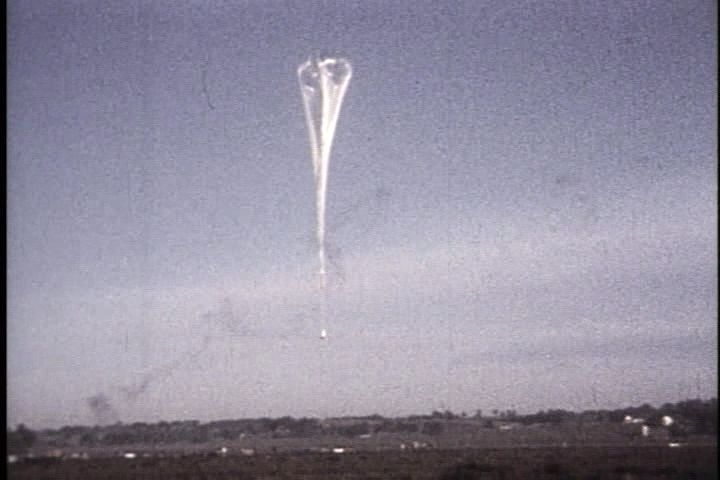
In the late 1940-ies started a project Skyhook (sky hook), in which the plastic balloons were used to send equipment into the stratosphere for the purpose of conducting scientific research. The first Skyhook balloon was launched on 25 September 1947.
Balloon Skyhook with stratoscope to study the Sun. Launched in 1957.
This ball had a solid silver sheath. In some models the balloons could reach a diameter of more than 30 m.
The first manned flight of such a balloon took place in 1949. Project Rockoon, in 1952, used a Skyhook balloon to launch small rockets Deacon at an altitude of about 70 000 feet (21 000 m) over the Arctic waters. 7 September 1956 at the University of Minnesota was launched a giant Mylar balloon (developed by the Corporation GT Schejeldahl Northfield, MN), who set an unofficial altitude record for unmanned balloons is equal to 145 000 ft (44 000 m) .
Project 119L or MOBY DICK
The project "Moby dick" was an intelligence operation of the U.S. air force during the cold war. Large balloons, equipped with cameras, had to fly over the Soviet Union.
The launch of the balloon MOBY DICK in Holloman AFB (nm) with the covered wagon
This project became the stepping stone for many other similar projects of the U.S. army.
WS-119L (aka the Gopher, he Genetrix)
Balloons were used by the U.S. army to flight with great aerofotografichesky units over enemy territory (in particular, the Soviet Union). Initially testing these devices was carried out on the territory of the United States (air force base in Alamogordo (new Mexico), as well as in the States of Montana, Missouri and Georgia).
Balloon project GENETRIX during startup
The first launches took place in 1955. To provide cover balls in this project was run simultaneously with meteorological balloons. From 10 January to 6 February 1956, was issued a total of 516 tall vehicles with five different pads: Gardermoen (Norway), Evanton (Scotland), is Oberpfaffenhofen and Giebelstadt (West Germany) and Incirlik (Turkey).
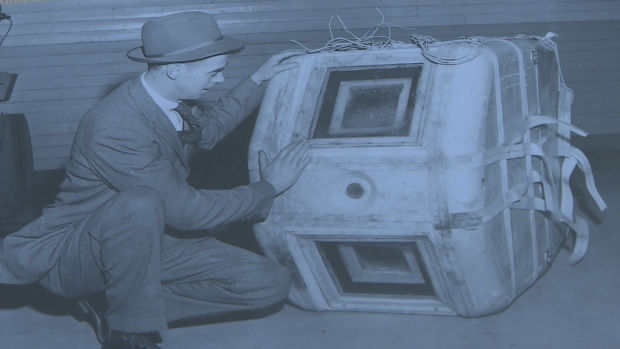
David McPherson-senior posing with equipment that he found in the woods in 1962, before the canadian military took him away. Fifty-five years later it was established that it was an American spy camera, which was flown by balloon.
Project Grab Bag
The project "Grab Bag" ("Bag") was a program of sampling of the air, conducted by the United States from 1956 to the early 70-ies of the monitoring in the stratosphere of above-ground testing of nuclear weapons in the Soviet Union. Special equipment mounted on a balloon, took samples of stratospheric air were pumped into a special container powerful pump. At some point the ball down from the height of 20 to 30 kilometers to one or two and dropped by parachute hardware that the flight was intercepted by a spy plane, and the balloon, freed from the burden, moved up and somewhere in the stratosphere burst. Debris such balls later fell to the ground and sometimes taken for the remains of alien ships. I wonder what getting parts collected radioactive materials on the ground gave rise to the idea of mandatory increase in the radioactivity of the landing site of a UFO.
There were also a number of projects devoted to the preparation to space travel. Here are a few examples.
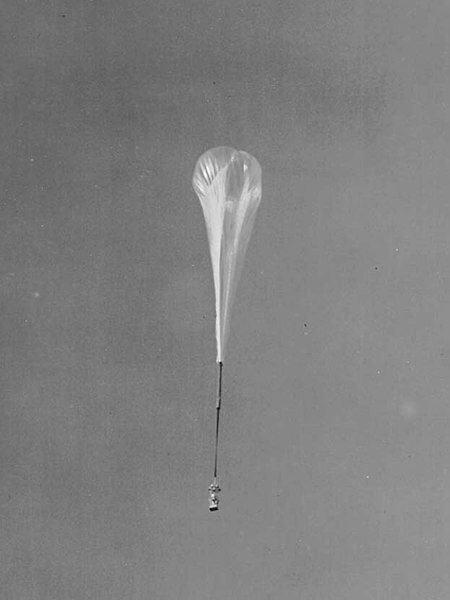
ManHigh
Balloon rising over the airport Fleming field Balloon ascending over Fleming Field (Image: USAF)
In 1957-1958, the U.S. air force conducted a series of stratospheric flight at the altitude of about 30 km, called "Man High" (original name "Daedalus"). The project was implemented by the center of development of missile armament of the air force and can be found here a field laboratory located on a U.S. air force base Holloman in new Mexico.
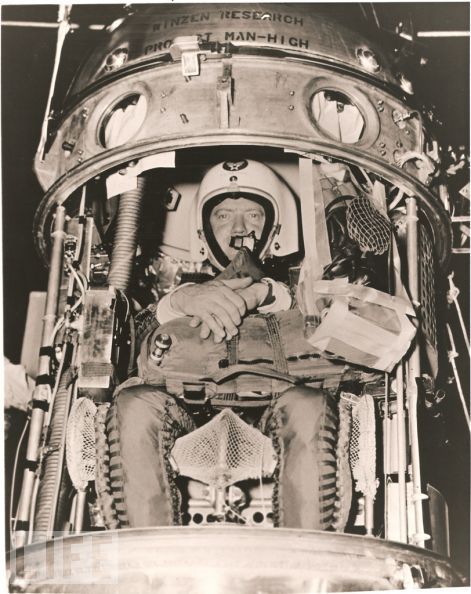
Captain Joseph Kittinger in the last moments before closing the capsule
The objectives of this project was to test life support systems, monitoring the status of the pilot, ejection and landing, the study of cosmic radiation and the effect of conditions of high-altitude flight on the human body.
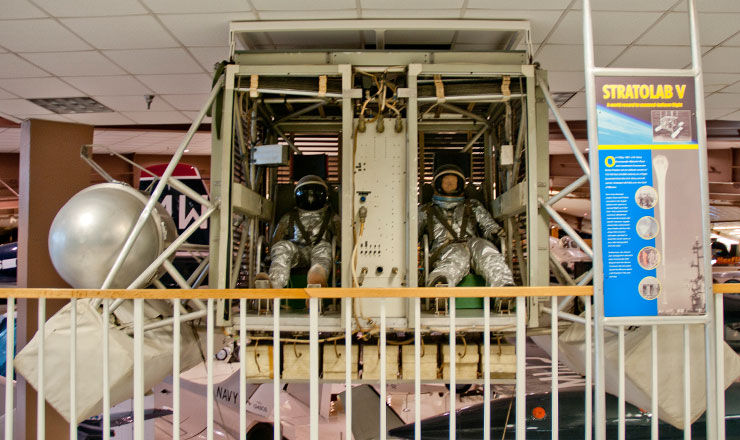
Project Strato-Lab
This program is sponsored by the U.S. Navy in the 1950s and early 1960s. Its purpose was to carry out observations and experiments in the upper stratosphere using balloons. The project has made a significant contribution to the manned space program and the development of methods of forecasting and monitoring the activity of solar flares.
The HIBAL program
Joint us-Australian initiative to monitor atmospheric radiation levels using large silver balloons equipped with sensors in the period from 1960 to 1969.
Each balloon was equipped with a capacity of 180 kg, followed by a light aircraft, which was tasked to monitor it and run it 12-foot parachute with radio signals.
Rockoon
The word Rockoon is derived from the English words "rocket" (rocket) and "balloon" (balloon). In the course of this project were delivered to the experiments for launching rockets from balloons in the upper atmosphere that allowed them to achieve higher points than when launched from land. The first experiments took place on 1 March 1949.
Photo design immediately after launch from the ship off the coast of Greenland, 1955.
This technology is now adopted as a principle of delivery of cargo to space ships.
Now stratospheric balloons used by ham radio (Amateur radio high altitude ballooning - ARHAB), weather services (including airports), scientists for pollution monitoring, photography or videography and other studies (e.g., project BARREL (Balloon Array for Radiation belt Relativistic Electron Losses: Grid of balloons to measure relativistic electron losses of radiation belt) or project Loon, invented by Google to provide Internet users around the globe), and many enthusiasts within the school or personal projects.
Hams first started this ball 15 August 1987. The balloon is usually attached various sensors, cameras and transmitters.
The weather service also used these balls since 1896, when the French meteorologist Leon de Teissere Board released hundreds of balloons from his Observatory in Trappes (France), which led him to the discovery of the tropopause and the stratosphere. Now weather balloons are launched around the world, usually twice a day (00:00 UTC and 1200 UTC) but sometimes produce additional runs.
Thus, many balls over the years was launched in the sky, and many of them in some circumstances could be mistaken for UFOs. In particular, they could be the reason for observing bright flashes of light, glowing spheres, giant ships "the size of a house", attacks of UFOs on aircraft UFO with bright red lights at the bottom etc. There is a logical view that the U.S. government not only fought with rumors about UFOs, but encouraged massive interest in flying saucers, to provide cover for their projects as among the local population and enemy territory.
Translated by «Yandex.Translator»
Log in or register to post comments