
| Added | Thu, 06/10/2016 |
| Sources | Пономарев А.А. "Фотофишки для цифровой и пленочной фотографии", 2010
|
| Феномены | |
| Version type |
There are a number of defects specific to film images. They are connected with the peculiarities of the film and principle photo.
The film in essence is a strip of transparent synthetic plastic, supported on her a photosensitive layer of chemical substances that can alter its transparency or properties under the action of light.
The first defect in the film can nazvati its ability over time to Shine. This photos on expired film work faded, foggy or not work at all. Natural illumination of the film occurs as a result of natural background radiation or cosmic radiation. Exposed film is also afraid of heat and moisture, from which the captured image can also appear defects.
Have an overdue film can also exhibit other defects. For example, dots or stripes of green and off-green shades.
The film also share the shooting conditions. Nepravilnoe the use of film can cause unusual color tones. If, for example, a film for artificial light to use for shooting in daylight, the received image is to take a bluish tone.
Features of the mechanisms of film cameras can also give various defects in the pictures.
For example, unbalanced or broken in the film transport mechanism can give a double image (multiple exposure) acceptable overlap of personnel. If the camera body is not sealed and violated its opacity, the part of the image may be overexposed (bright spot or spots). Another defect can be considered scratch - marks from the rollers pulling on the tape are distinguishable in the slanting rays of light. Stripes in the first frame of film (slide film, light orange or striped, and the negative film — dark stripes) appear due to constrcutive features cassettes with the tape wrong with her treatment in the hole in the cassette light.
Defects are divided according to the following criteria.
- The location on the negative. The defect may reside on the media (in this case glass), on the emulsion or in the emulsion layer. It can be chips, cracks, deep scratches, etc.
- Origin. It may be different kinds of mechanical damage and contamination (foreign objects on the surface of the emulsion, dust, fingerprints, gelatinous, or grease contamination, the dried streaks of water, dyes); optical defects of character, which were recorded on the emulsion during a photo shoot (glare internal lens surface; a parasitic illumination, the glare formed by the petals of the holders of inserts in magazines).
- By the nature of the defects in the image. Defects in negatives vary in:
- form;
- structure;
- size (depending on the frame size);
- brightness (optical density);
- the luminance profile;
- the degree of transparency of the defect (opaque, transparent, variable, or edge transparency);
- the location of the defect information on saturated areas of the image and level of detail of the masked area.
We can distinguish the following defects
1. Destruction, or decomposition of the photo-emulsion layer.
2. Reticulation — a violation of the integrity of the emulsion layer from wrinkling and cracking.
3. Detachment of the emulsion.
4. Scratches on the emulsion.
5. Scuff or abrasive damage.
6. Physical defects "wet process".
7. Pollution.
8. Biodeterioration.
9. Optical defects.
10. Films of different types (collodion silver, dichroic and edge veils) on the emulsions that affect the optical properties of the image.
11. Damage of a mechanical nature (chips, cracks, fragmenting, etc.) that caused the violation of the integrity of the media and emulsions.
We list these defects.
On the negative
Voile, two-tone, square. 1. Developing solution is contaminated with fixer. 2. Manifestation too warm solution. 3. For too long expression. 4. The photographic material after development are insufficiently washed. 5. The fixing solution is contaminated with developer. 6. Treatment in exhausted fixer. 7. Fixation in a warm solution. 8. Incomplete fixation. 9. In showing the solution of many solvents of silver halide: sodium sulfite, potassium Rodenstock.
Veil purple*. 1. The photographic material is insufficiently washed between developing and bleaching solutions.
* (Defects marked with an asterisk* apply only to color photographic materials.)
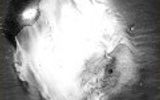
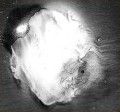
The veil of gray, evenly covering the entire photographic material. 1. Old or improperly stored material. 2. Manifestation too warm solution. 3. Processed in contaminated developer or developer containing substances that cover. 4. Processing highly concentrated or having an insufficient amount of potassium bromide to the developer. 5. Long manifestation. 6. Weak white light acted on the photographic material when it is charged in the cassette or at the time of development. 7. Photos when shooting was exposed to too much exposition.
Sluggish image. 1. If the image density is normal, the reason in nezapravlenny overly exposed photos when shooting. 2. If the exposure and the manifestation of right, the shoot took place in cloudy weather, or the subject had a small brightness range.
The coarse image. 1. A highly sensitive photographic material. 2. Shooting with high exposure. 3. Processing fast developer. 4. Developing solution had elevated temperature. 5. Treatment in exhausted developer. 6. The material quickly dried.
Details a white or gray color appeared to be painted*. 1. Shooting in mixed lighting - fluorescent and incandescent lamps.
The details are extraneous color*. 1. When shooting color arose reflexes, because the object was covered by additional svatmarama.
Mirror-inverted image. 1. Shooting on the film from the substrate.
The image has a reddish tone (positive)*. 1. Shooting under incandescent photographic material, balanced to daylight.
The image has a bluish tone (positive)*. 1. Shooting in daylight on a color photographic material, balanced to artificial light.
Negative and positive at the same time. 1. During the appearance on photographic material into the white light. 2. The exposed photographic material during processing, in exhausted fixing solution.
Frames of photographic film, exposed recently, was denser than frames exposed for a long time. 1. The film was in the camera at elevated temperature and humidity, as a result there came the destruction of the latent image.
Contrast. 1. If the details in the shadows do not exist, inflated the day of the manifestation of the material insufficiently exposed when shooting. 2. If the exposure and the manifestation of right, the survey was carried out at excessive contrast light or object had a very large brightness range. 3. Incorrectly selected color filter for shooting.
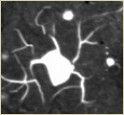
Line dark, sharply defined, branched or dark spots with blurry edges - the result of electrical charges. 1. Unsatisfactory storage conditions of the material. 2. The dry film was exposed to friction in the tape or the camera. 3. A sharp temperature change between the conditions of storage and use of the photographic material.
The negative double loop - blurred image. 1. When shooting, the camera vibrated. 2. The object moved very quickly. 3. Incorrectly selected shutter speed when shooting a moving object.
Negative with milk color. 1. Incomplete fixation of the photographic material. 2. The fixing solution is weak or exhausted.
Blurred image. 1. Wrong made fire of the lens for sharpness. 2. Faulty rangefinder camera. 3. Inaccurate scale pickup lens for sharpness in the camera. 4. Incorrectly identified the distance to the object with the tip of the lens for sharpness at metrazhnoj scale. 5. Not the same as the plane of the photographic material in the camera with the point of pickup lens for sharpness. 6. Rozniakowski lenses on the camera is not aligned. 7. Shooting with a cold or the contaminated lens. 8. Used poor quality filter.
Monochrome or two-color image*. 1. Shot through a thick filter.
The ghosting in the frame. 1 Shooting without a polarizing filter objects that have flashing items: glass, polished wood, water, etc. 2. The lens came light sources.
Precipitation on the photographic material. 1. White, gray, matte to granular (calcium grid) - was used hard water for solutions or for flushing. 2. Yellowish-white or whitish-gray traces of sulfur, aluminum, and other substances that had fallen from the malformed fixing solution or contaminated, depleted, and long kept open at an elevated temperature developers. 3. Brown, with metallic luster, often slimy sediments in the processing of photographic material in the solution, the surface of which is formed by a thin film of oxidation products of the developer or developer contaminated by micro-organisms that create sulfides in the form of a brown patina. 4. Precipitation of silver, gleaming in the reflected light appear on the photographic material during its contamination with oxidation products containing silver. 5. Grey precipitation with weak metallic sheen appear on the photographic material processed in the developer containing a solvent of silver (a large amount of sodium sulfite, potassium Rodenstock, etc.).
The fingerprints on the photographic material. 1: emulsion layer touched with wet or dirty hands.
The increased density of the image. 1. Inflated the time of development of the photographic material. 2. High temperature developing solution or its concentration is increased.
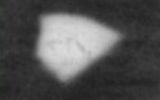
The edges of the frame image of low density. 1. Applied too narrow or too long a lens hood. 2. Shooting a lens with very short focal length. 3. Lens when shooting was covered by outsiders, the subject.
Stripes on weakened or strengthened the image. 1. Before the process of weakening or strengthening image the photographic material is poorly flushed.
Stripes of dark, transverse, starting at the perforations. 1. The film was treated in an energetic or warm developer, who jets through the perforations operated on the emulsion layer. 2. The film was washed in warm water after development.
The strip is slim and light. 1. The manifestation of the material solution is not stirred, bubbles of air were sliding on the emulsion layer.
Stripes black, longitudinal. 1. The film is scratched by the Burr in the slot of the cassette or on the walls of the channel of the camera. 2. Film careless rewinding. 3. Film wound too tight or it was pulled when winding in tape.
Reduced image density. 1. Lack of time manifestation of the photographic material. 2. Low temperature of the developing solution or its concentration is reduced.
After shooting on the photographic material is blank. 1. Lens while shooting was closed with a lid. 2. Not open the shutter. 3. The photographic material is processed in a fixation solution instead of showing.
Spot gloss on the emulsion layer. 1. Time of drying emulsion layer stuck to the substrate of the other films.
The spots are small in the form of honeycombs. 1. The manifestation of the material solution is not stirred. As a result, an emulsion layer, traces of air bubbles. 2. In processing the photographic material in a very alkaline developer and acid fixing solution the gas is released.
The spots are small, bright crater. 1. The photographic material is insufficiently washed between energetic manifestation and acid fixation. 2. Fixation in a solution, which had overestimated the amount of sodium thiosulfate. 3. During drying the emulsion layers were destroyed by bacteria or insects.
Mold stains. 1. Photographic material kept in a damp location.
The spots are transparent. 1. The photographic material before its manifestations were splashes of fixative.
Spot light. 1. When you transfer the photographic material from the cold into a warm room emulsion layer is fogged.
Spot light, with dark borders. 1. On the emulsion layer has drops of water after drying the photographic material.
Spots dark. 1. On the emulsion layer before processing it were splashes of the developer. 2. To the emulsion layer stuck undissolved crystals of the developing agent.
Spots colored. 1. Blue, purple and brown - from the contact of the processed photographic material with iron. 2. Dirty-purple and gray-brown, with a silvery hue from lack of fixation or fixation in a solution containing a lot of silver. 3. Greenish processing of a spoiled tanning fixation solution. 4. Yellow and brown with a silver tint - incomplete fixation of the adhesion of the emulsion layer to a substrate or other surface, from poor rinsing after fixation, when during storage in an emulsion layer is formed of sulphurous silver.
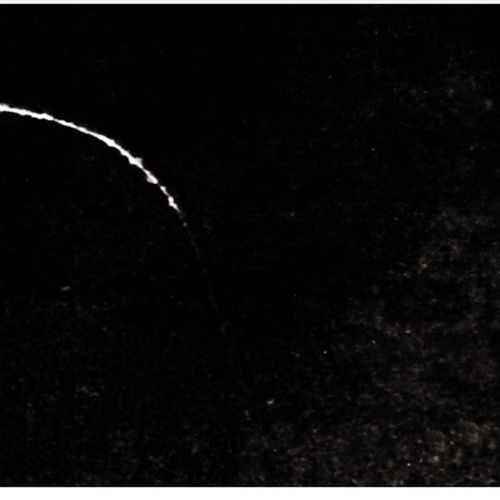
Spot in the form of an arc. 1. During shooting during backlighting by the sun's rays hit the edge of the lens.
Spot in the form of a star. 1. When shooting against the sun, the lens was badly for diaphragm.
The destruction of the latent image - photorelease. 1. From acquisition to manifestation much time has passed. 2. In an exposed photographic material acted warm and humid air. 3. When storing exposed photographic material in a humid and warm climate was not used moisture-absorbing substance and the special packaging.
Dual image in one frame two or more images. 1. Faulty transporting or blocking the mechanisms of the camera. 2. Swapped the cassette with the photographic material.
Grey table in the image is color color, dense fields - one color, bright and other*. 1. Substandard the reserve balance of the contrast of the layers. 2. Incorrectly showed the photographic material.
The twist of the film. 1. The film dried. 2. Long kept in a warm and dry air.
Traces of drops on the photographic material. 1. Used hard water when flushing. 2. The photographic material prior to drying is not handled in m OP-7 or OP-10.
The adhesion of film. 1. Photographic material kept in a humid environment. 2. When peremanivanie film on its surface gets wet.
Point rough on the emulsion layer. 1. During drying of the emulsion layer of the photographic material hit the dust.
A black stripe crosses the image. 1. Through the damage in the camera or in a cassette for photographic material has fallen light.
The emulsion is cracked - the phenomenon of reticulate. 1. The photographic material was treated in a warm developing solution. 2. There was a big difference in the temperatures of the solutions. 3. Too long rinse in cold water. 4. Drying of the photographic material at high temperature. 5. Emulsion layer in a wet kind of cold. 6. In manifesting the solution was a lot of caustic alkali. 7. Very acidic fixing solution. 8. On a warm emulsion layer acted cold air. The emulsion is damaged. 1. Rough handling of wet photographic material in the processing solution or during drying.
The emulsion has acquired the marble-like structure. 1. During processing of the photographic material developer is not stirred.
The emulsion is bubbling. 1. The photographic material was treated in a very acidic fixation solution. 2. Very acidic stopping solution. 3. A color photographic material was washed in very soft water.
The emulsion melted. 1. The photographic material was treated in a warm solution or washed in warm water. 2. Developing solution was strongly alkaline. 3. Drying was carried out at high temperatures.
The emulsion is fragile. 1. The photographic material is overdried, was dehydrated.
On the positive
Veil yellow. 1. Excessive manifestation of the paper. 2. The manifestation of the elevated temperature of the solution. 3. Developing solution is exhausted or contaminated. 4. In developing the solution insufficient bromide of potassium. 5. Between the manifestation and fixation of photographic paper insufficiently washed. 6. Stopping solution is exhausted, or improperly prepared. 7. The fixing solution is exhausted, too sour or exposed to high temperatures. 8. The photo paper is not enough recorded. 9. Photo paper not processed in the stop solution, and fixer contained only sodium thiosulfate.
The veil on the edge of the paper. 1. Warranty period paper has long expired. 2. The photo paper was stored in warm, damp, under the influence of harmful gases. 3. Bad packaging paper.
Veil purple*. 1. Photo paper insufficiently washed between manifestation and bleaching. 2. Developing solution is contaminated with fixer. 3. Old photo paper.
Veil pink*. 1. Photo paper is too long washed before drying.
The veil of gray, evenly covering the entire surface of the paper. 1. Old or improperly stored paper. 2. The manifestation was carried out at a high temperature of solution. 3. Developer too concentrated or insufficient quantity of bromide of potassium in solution. 4. Contaminated developer. 5. Illumination through the defective filter of a laboratory lamp. 6. Stray light from the photographic enlarger. 7. Photo paper, when printing was subjected to very long exposures. 9. The manifestation of photographic paper was frequently removed from the solution for observation of the image.
Sluggish image. 1. If the image density is normal, then completely developed photo with too much exposure. 2. If the exposure and the manifestation of normal, then printing was conducted with a slow negative or incorrectly matched photo paper for contrast.
The coarse image. 1. Enlarger without lens light. 2. Printing with gruposeincentivos. 3. Too much magnification of the image. 4. The photo paper is processed in solution or in the water, which formed an undesirable crystalline residue on the emulsion layer.
Details yellow low density*. 1. Tanning solution had the higher concentration of formalin.
Mirror-inverted image. 1. The printing side of the substrate negative.
Negative and positive at the same time. 1. The manifestation on* photo paper acted weak light. 2. The photo paper was lit when processing in exhausted fixer.
Contrast, shadow details are missing. 1. The photo paper is properly matched to the negative. 2. Long enough manifestation of exposed photographic paper. 3. Treatment cold developer with a high content of bromide of potassium. 4. Printing with high-contrast negative.
The contrast is reduced. 1. Insufficient manifestation of the paper. 2. Manifestation in the depleted solution. 3. Manifestation in a solution with a lower temperature. 4. Printing with a slow negative.
Red spots and points*. 1. The photo paper is too old.
The saturation of color is insufficient*. 1. Treatment in exhausted developer. 2. Lack of time of manifestation or the solution temperature is below normal. 3. Incomplete bleaching of paper.
Blurred image. 1. Printing with blurred negative. 2. Lens photographic enlarger installed correctly on the sharpness. 3. Photographic enlarger lens is fogged or dirty. 4. Enlarger vibrate when typing. 5. There was little contact between the negative and photographic paper in a copying frame, the uneven pressure. 6. The negative and paper during printing is located not in parallel. 7. Negative or warped photo paper folded.
Precipitation on photographic paper. 1. White, grey, Matt - when using hard water solutions and for rinsing. 2. Yellowish-white or whitish-gray traces of sulfur, aluminum, or other substances that fell from improperly prepared fixing solution, developers of contaminated, depleted or standing for a long time at an elevated temperature.
The increased density of the image. 1. Improper exposure when printing. 2. For too long expression. 3. Developing solution is very concentrated. 4. A developer with a high temperature.
Yellowing of photo paper. 1. Treatment in exhausted fixer. 2. Stopping solution is too acidic or long in this treatment. 3. Fixer very acidic. 4. The photo paper is insufficiently washed before drying. 5. If the sticker paper used is acidic glue.
The edges of the frame image of low density. 1. The lamp in the photographic enlarger or copying machine is installed incorrectly. 2. The format of the negative more than the format expected by the photographic enlarger. 5. The lens of the photographic enlarger is covered with something.
Stripes are black. 1. The paper is sloppy cut before the symptoms. 2. Photo paper before symptoms rubbed against a hard surface.
Reduced image density. 1. Improper exposure when printing. 2. The photo showed less than it should. 3. Developing solution is exhausted. 4. Developer with a lowered temperature.
When storing the image is destroyed. 1. Photo paper insufficiently fixed and washed. 2. On photo paper for a long time acted in the light of day. 3. Positive were stored in adverse temperature conditions.
Come bubbling slide of the emulsion layer. 1. Treatment in very acidic fixer after strong alkaline developer. 2. Stopping solution with high acidity. 3. Fixer excessively concentrated. 4. Processing fixer and in water of different temperatures. 5. Rinse in warm water. 6. Final rinse too long.
The spots are small, crater. 1. During drying, the emulsion layer is destroyed by insects or bacteria. 2. Insufficient washing between energetic developer and acidic fixer. 3. The fixer is very concentrated.
Spot after glossing. 1. Dirty metal plate or glass, which prikalyvalo photo paper. 2. Surface for compacting had damage. 3. During rolling between the emulsion layer and a glossy surface formed bubbles. 4. The photo paper is much zagublena: 5. Photo paper for polishing hot enough zagublena. 6. Pancevo is very fresh photo paper. 7. Photo paper before polishing too long washed in water. 8. Soda solution, which was treated with photo paper, poorly washed from the emulsion layer. 9. Glossing on the glass in too dry air. 10. Glossing on very hot plates. 11. Insufficient clamping the paper to a glossy surface.
Spots of light and dark in the image. 1. Very tight clamping of the film to cover the glass in the frame negativemargins in the photographic enlarger. Having Newton's rings - a rainbow painted areas.
Spots on a substrate of photo paper. 1. Treatment in very acidic fixer. 2. The photo paper is too long was in a stopping solution containing acetic acid.
Dark spots on the image. 1. On the emulsion layer of the photographic paper before processing it drops the developer. 2. To the emulsion layer stuck undissolved crystals of the developing agent.
Spots colored. 1. Blue and purple from the contact of the paper with the iron when it is processed. 2. Dirty-purple and gray-brown, with a silvery hue from lack of recording paper or processing in a solution containing a lot of silver. 3. Greenish - when processing a spoiled tanning fixation solution. 4. Yellow and brown - if the emulsion has stuck to some surface, hindering the treatment process, or photo paper was poorly rinsed after fixation, resulting in an emulsion layer having a silver sulfide.
Spot in the form of an arc. 1. Improperly installed lamp in the photographic enlarger.
Dual image. 1. It is a mistake on a single sheet of paper printed double-negative.
Gray images. 1. Printing with low-contrast and transparent negative. 2. The photo paper is properly matched to the negative. 3. Old or improperly stored paper. 4. Stray light when printing. 5. Lens photographic enlarger contaminated. 6. Excessive exposure when printing, and a short demonstration of paper. 7. For too long expression. 8. Treatment in a warm developer. 9. In developing the solution insufficient bromide of potassium. 10. Excessive fixation of photographic paper in a fresh solution and very hot polishing.
Mesh red tone*. 1. Old or improperly stored paper.
Twisting the paper. 1. Old photo paper on a thin substrate in the developer or is treated in strongly alkaline solution. 2. Old, or very zagublena photo paper dried at a high temperature. 3. The photo paper was dried near a heating device. 4. The photo paper was stored in a room with dry and warm air.
Tone tan*. 1. Incomplete bleaching of paper. 2. Old photo paper.
The yellowish tone. 1. Photo paper long cultivated in the old developer. 2. In manifesting the insufficient solution of sodium sulfite. 3. Photo paper is often out of the developer for viewing images. 4. The photo paper is insufficiently washed before fixation. 5. The fixing solution is exhausted. 6. When fixing or washing is sticking to the paper.
The greenish tone. 1. The photo showed a long time working solution. 2. The developer was an excessive amount of bromide of potassium.
Tone purple. 1. The paper continued to manifest itself in a fixation solution. 2. Emulsion layer stuck to a substrate of another sheet of paper and after development is treated in the fixer.
The color reproduction is distorted*. 1. Improper corrective filters for image printing. 2. The negative balance of contrast. 3. Photo paper with the wrong balance of contrast. 4. Broken technological processing mode paper.
The emulsion has cracked. 1. Treatment in a warm developer. 2. In the processing solutions had a very different temperature. 3. Photo paper for too long, washed in cold water. 4. Drying at high temperature. 5. The wet emulsion layer is frozen. 6. On a warm emulsion layer acted cold air.
The emulsion melted. 1. Treatment in warm solutions or rinse in warm water. 2. Developing solution strongly alkaline. 3. Fixation in extremely acid solution after short rinsing in water. 4. Photo paper is very long washed before drying. 5. Drying at high temperature.
The emulsion is fragile. 1. Photo paper dry. 2. Drying near heat in case of insufficient humidity.
On the slide
The blue veil*. 1. Insufficient washing of the film after color appearance.
Veil yellow. 1. A large amount of sulfuric acid in the whitening solution with potassium dichromate.
Veil dense. 1. Rudoproyavlenie in the first developer. 2. Lack of exposure in photography is underexposure.
The coarse image. 1. High-sensitive photographic film. 2. Film in the first developer was treated with a lack of time, and the second being overweight. 3. Used hard water.
Details white and grey painted*. 1. The film is substandard for the balance of the light sensitivity of the layers. 2. The shooting happened in the lighting, which did not correspond to the balance of the layers of film. 3. The survey conducted in mixed lighting: natural and incandescent lamps. 4. An imbalance of the layers of film.
Details monochrome reproduced in different colors*. 1. Substandard film. 2. The lighting conditions did not match the properties of the films. 3. The interval of brightness of object of shooting more photographic latitude photographic film. 4. Violated the technological process of processing of photographic film.
Items with an extraneous color*. 1. When shooting used light sources with different color temperatures. 2. For details of the object acted reflections from colored surfaces - colored reflexes.
The image is monochrome or two-color*. 1. Shooting through a filter that absorbs one or two areas of the spectrum.
The contrast is elevated. 1. Large brightness range of the subject. 2. Too short for processing in the first developer. 3. The temperature of the first developer was below normal. 4. Excessively vigorous mixing of the first developer during the processing of photographic film.
The contrast is low. 1. Small brightness range of the subject. 2. Too long processing time in the first developer. 3. The temperature of the first developer was above normal. 4. Rudoproyavlenie in the second developer. 5. Insufficient mixing of the second developer during the processing of photographic film.
The edges of film perforations in opaque. 1. Rudoproyavlenie film in the first developer. 2. The first developer is exhausted or has a lower temperature.
The edges of the film with the perforations clear. 1. Insufficient illumination of the photographic film before the second manifestation. 2. Rudoproyavlenie film during the second manifestation.
The lack of transparency of the image. 1. Partial destruction of the negative image in the bleaching of photographic film.
The density increased. 1. Lack of exposure in photography is underexposure. 2. Completely developed photo film in the first developer.
The density decreased. 1. Exaggerated exposure in photography - overexposure. 2. Film pereplavleni in the first developer. 3. Insufficient illumination of the photographic film prior to processing in the second developer.
When viewing film in reflected light visible brown hue*. 1. Incomplete bleaching and fixing of photographic film. 2. Poorly washed films. 3. Storing film in a warm and humid air. 4. Color film long been under the influence of light.
The tone of blue*. 1. Completely developed photo film in the first developer. 2. In the processing of photographic film, the first developer is not stirred and the second was mixed. 3. During the processing of photographic film both a developer is not stirred.
The tone of yellow-brown. 1. The film is not sufficiently processed in the whitening solution. 2. Too long treatment in the whitening solution. 3. Bleaching solution is very concentrated. 4. Clarifying solution is exhausted or insufficient in this treatment. 5. Manifesting solutions are exhausted. 6. Insufficient intermediate rinsing after the first manifestations or low water temperature.
Tone yellow-green*. 1. Rudoproyavlenie in the second developer. 2. Treatment was carried out in the second developer at a low temperature. 3. Enough vigorous mixing of the second developer.
Tone yellow*. 1. Film pereplavleni in the first developer. 2. In the processing of photographic film, the first developer was stirred, and the second - not stirred.
The greenish tone*. 1. The first manifestation was carried out at low temperature. 2. Film designed for processing in amicalola developer, treated in solution with feniton-hydroquinone.
The reddish tone*. 1. Shooting with incandescent lamps on a photographic film designed for daylight.
Tone purple*. 1. The film is insufficiently washed between developing and bleaching solutions. 2. Developing solution is contaminated with sodium thiosulfate.
The bluish tone*. 1. Shooting in daylight on a photographic film designed for incandescent bulbs. 2. Lack of exposure in photography. 3. Short treatment time in the first developer:
The film is transparent. 1. Photographic film exposed to the first manifestations. 2. There was no exposure of photographic film to the second manifestation. 3. The film is not processed in a second developer.
A film with black spots. 1. The film was treated in the whitening solution having a high concentration of potassium dichromate.
Translated by «Yandex.Translator»
Related facts
Related news
Related articles
Log in or register to post comments

















































In this article author expresses his opinion and is not intended to offend or tarnish someone. Constructive discussion of the content of the article is encouraged. Not essential comments will be ignored. Comments that bear the offensive, as well as containing pornography, advertising and promotion (political, religious, etc.) are not permitted and will be removed by administrtation.
Comments
мортал комбат 2 на андроид [url=https://apk-smart.com/igry/draki/675-mortal-kombat-2.html]https://apk-sm... мортал комбат 2 на андроид
P.S Live ID: K89Io9blWX1UfZWv3ajv
P.S.S [url=https://druid.ru/bored/viewtopic.php?p=8753&sid=344706912453cae80bb98a59...Программы и игры для Андроид телефона[/url] [url=https://tonkostiosago.ru/izmeneniya-v-zakone-osago/stoimost-osago-i-koef...Программы и игры для Андроид телефона[/url] f631221