| Added | Mon, 12/12/2016 |
| Источники | |
| Дата публикации | Tue, 21/06/2016
|
| Феномены |
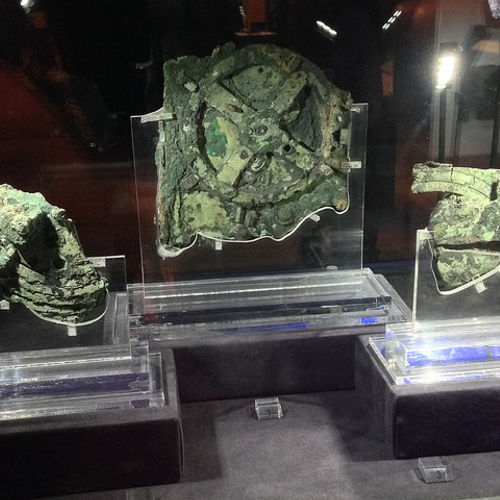
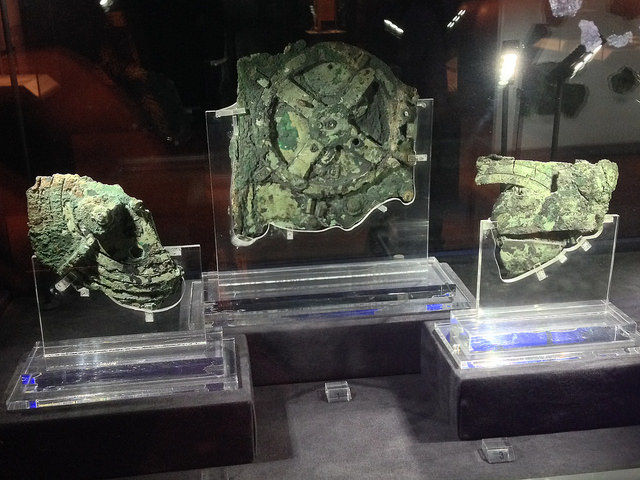
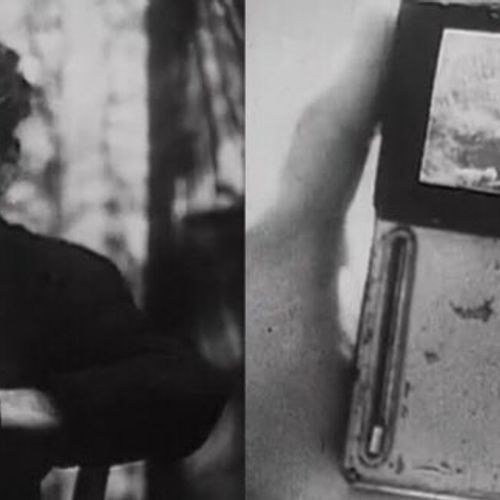
In 1901 off the island of Antikythera found the remains of a sunken ship and its cargo: a lot of bronze and marble statues, and glass and ceramic vessels. Among the finds was a small box, inside of which there were several dozens of bronze gears.
What they're dealing with, researchers understood far not at once – components are strongly oxidized and "caked" into one lump. Almost half a century remains of a strange device lay in the storerooms of the National archaeological Museum in Athens. Only in 1958, they again drew attention. Then the historian of science Derek de Solla Price, using snapshots of the mechanism in gamma and x - rays suggested that it could be a device for determining the position of the Sun and the moon. Later it turned out that with a lot of the Antikythera mechanism, it was possible to determine the position of mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn, as well as to predict eclipses.
"The mechanism was not a tool of the astronomer or astrologer, this was a device that could be used to teach understanding of the cosmos and our place in it. It is a kind of textbook on astronomy, which in the understanding of the ancient Greeks connected the movement of the sky and planets with the life of people and nature," – said Alexander Jones (Alexander Jones), a participant of the study, Professor of the history of ancient science from the University of new York.
He added that the device could be something more- for example, the device for training philosophers.
Translated by «Yandex.Translator»
Fragments a lot of the Antikythera mechanism in the National archaeological Museum in Athens. Photo: Dimitris Kamaras / https://flic.kr/p/zo79B6 / CC BY 2.0.
Translated by «Yandex.Translator»
Новости со схожими феноменами
Log in or register to post comments