| Added | Sun, 08/04/2018 |
| Sources | |
| Феномены | |
| Version type |
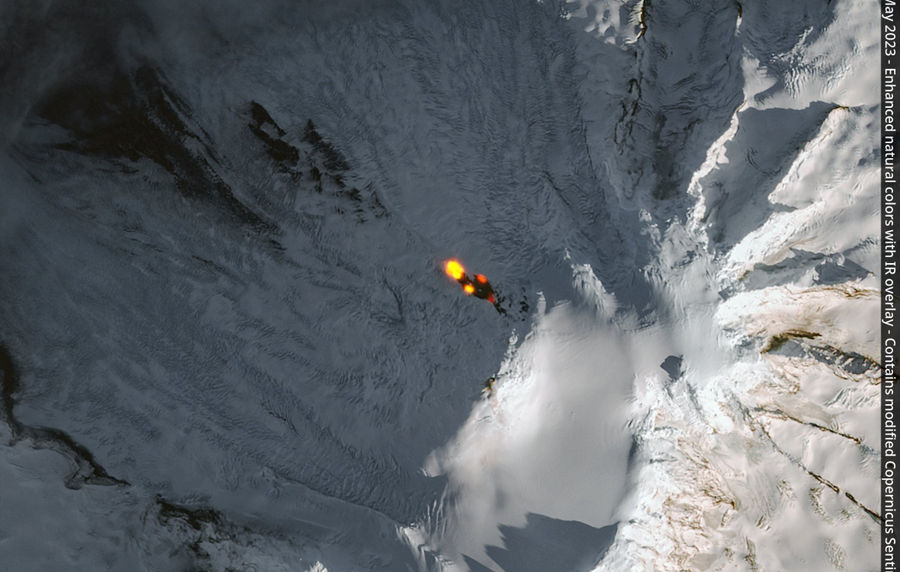
Volcano eruption — the process of emission of a volcano to the earth's surface hot debris, ash, outpouring of magma, which islevsel on the surface, it becomes lava.
The eruption may have a time period of from several hours to several years.
There are different classifications, among which are common to all types (sometimes referred to as after famous volcanoes where observed):
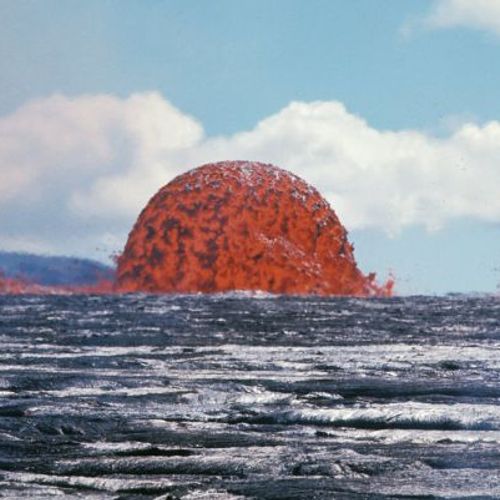
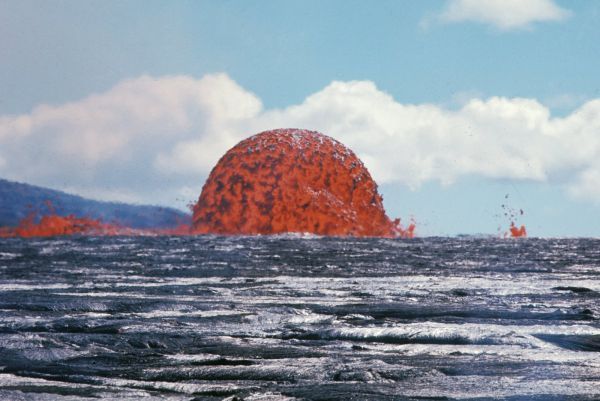
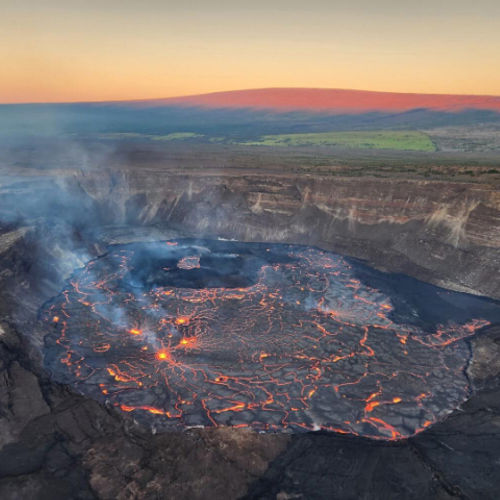
The Hawaiian type. Is characterized by effusion of liquid, highly mobile basaltic lava forming huge flat panel Board volcanoes. Pyroclastic material is virtually absent. During eruptions through the cracks fountains of lava ejected through faults in the rift zone of the volcano and flow down the slope flows a small capacity for tens of kilometers. During the eruption through the Central channel of lava ejected up to several hundred meters in the form of liquid pieces of "tortillas", creating the shafts and cones of spatter. This lava may collect in old crater, forming a lava lake.
Strombolian type. Associated with more viscous lava core, which is thrown different power of explosions from the crater, forming a relatively short and a more powerful lava flows. The explosions formed cinder cones and cables of twisted volcanic bombs.
Plinian type. A characteristic feature of this type of eruptions are powerful, often sudden explosions, accompanied by emission of huge quantities of tephra, forming pumice and ash flows.
Pulaski type. Pulaski type eruptions are characterized by the formation of a Grand cloud of hot avalanches (eruptive cloud or "scorching cloud"), as well as the growth of extrusive domes of extremely viscous lava. Eruptive clouds in the form of convective columns with well-developed turbulence are a source of infrasound and long-wave perturbations in the atmosphere.
Gas (phreatic) type. With this type thrown into the air fragments of hard, ancient rocks (new magma is not erupting), due to either magmatic gases, or associated with overheated groundwater.
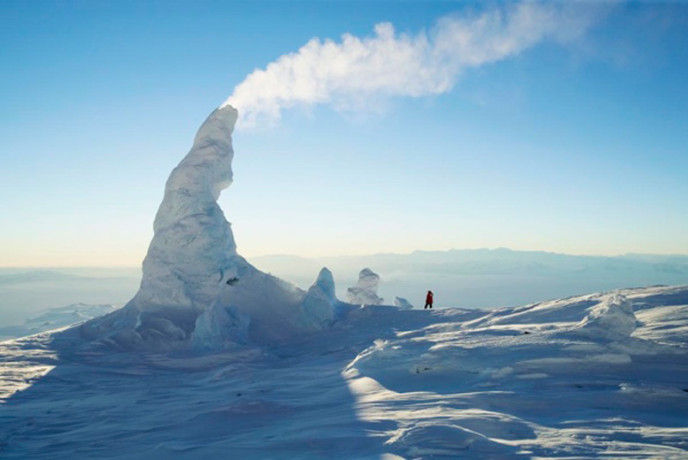
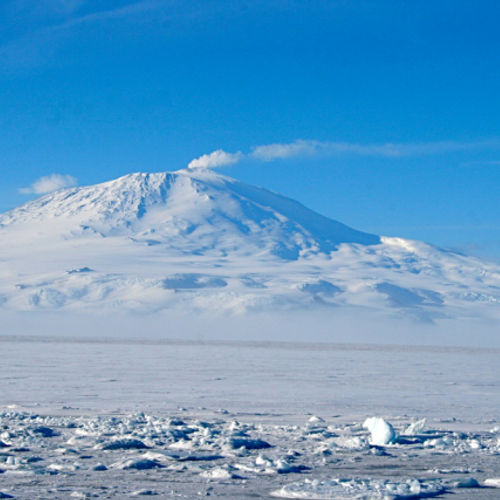
Ice-type. Relates to volcanoes under the ice or glacier.
The eruption of ash flows. This type was widespread in the geologic past, but this was not observed by man.
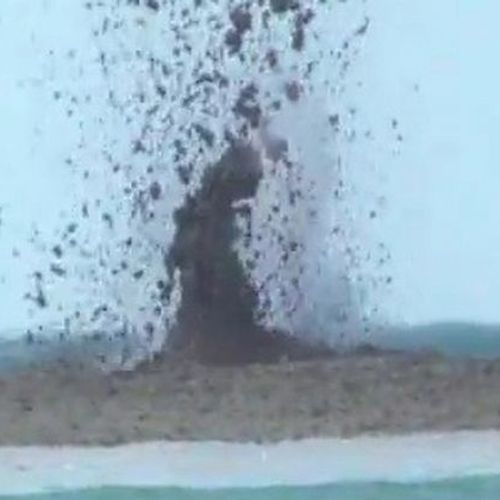
Gidroekologiya eruption. Occur in shallow-water conditions of the oceans and seas. They are distinguished by the formation of a large amount of steam arising from the contact of hot magma and seawater.
Icelandic type. Is characterized by the emission of very fluid basaltic lava with a content of pyroclastic material. Usually form a flat shield volcanoes. The eruption occurs along fractures.
"Crack of thunder". Occurs at dome volcanoes. The cracks that start to go from magma is lava, but not viscous. When the cracks reach the crater explosive eruptions occur (with explosions).
The eruption of some volcanoes can have only one type for a certain period of activity, while others may display an entire sequence of types of eruptions.
The eruption of water vapor — also a characteristic feature of post-volcanic stage. As the distance from the source of the water vapor is converted to hot emissions, is usually highly mineralized water in the form of a hot and heated sources. The sources are permanent or periodically releasing water. The latter are called geysers. The frequency of eruptions of geysers are usually very constant. The intervals of eruptions from the various geysers range from 10 min to 5.5 h. water Temperature +94--g-99° C. the Water of geysers is usually mineralized, contains salts of sodium, magnesium, calcium, silicon. In this regard, around the geysers are a frequent deposits in the form of porous calcareous or siliceous tuff.
Translated by «Yandex.Translator»
Related facts
Related news
Log in or register to post comments