| Added | Wed, 22/03/2017 |
| Sources | |
| Феномены | |
| Version type |
Standing wave — interference phenomena of waves propagating in opposite directions, in which the energy transfer is weakened or absent.
The elastic body can perform quite complex vibrations for which they contract, stretch, bend and twist. Vibrations of any elastic body can be represented as a combination of overlapping each other over simple normal fluctuations.
Examples of the standing wave can serve as the vibrations of strings, vibrations of air in an organ pipe, but in nature: waves Schumann (standing electromagnetic waves in the system "the surface of the Earth — ionosphere") and seyshi.
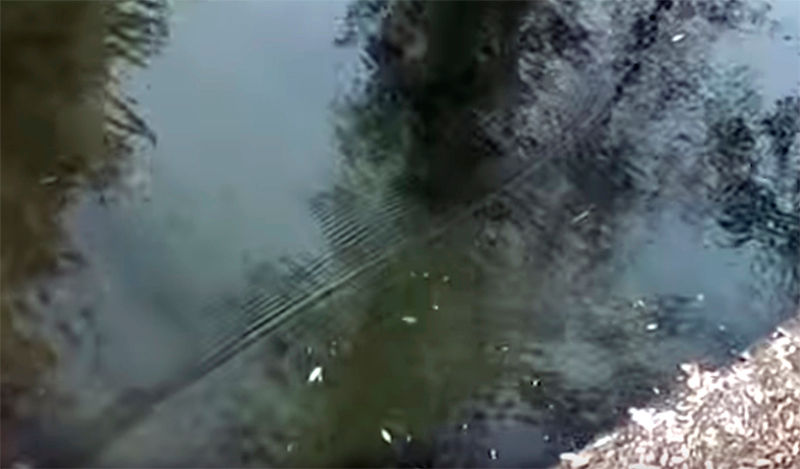
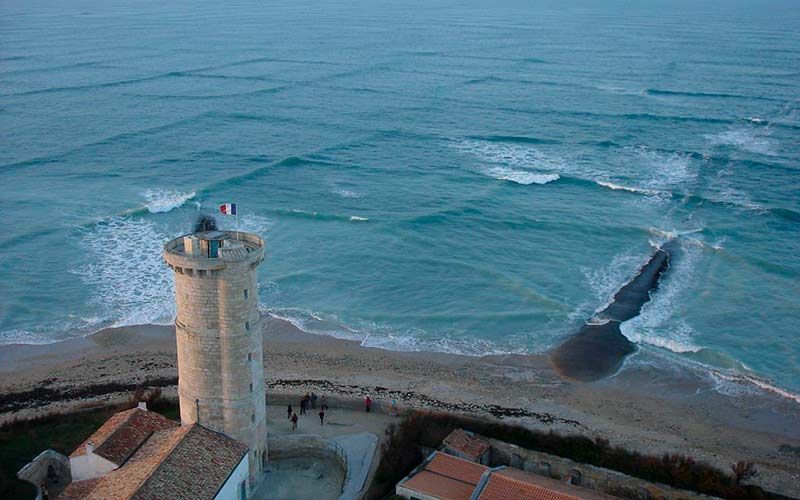
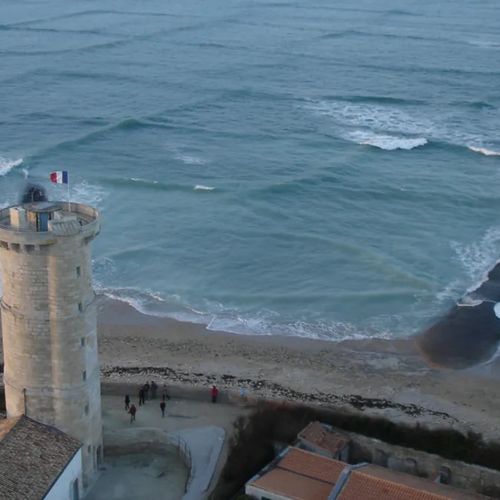
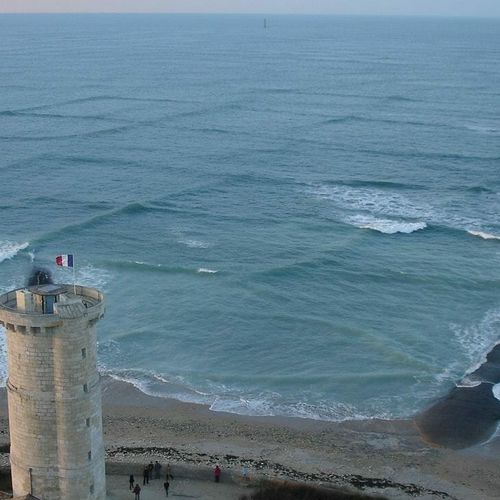
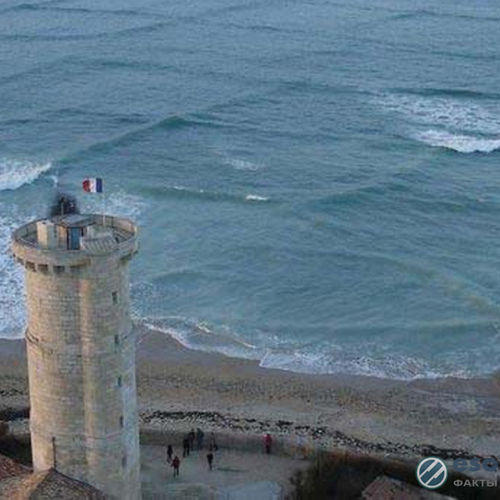
Seyshi (from the French Seiche) is the standing waves that occur in enclosed or partially enclosed waters. They are the result of resonance phenomena in the reservoir in the interference of waves reflected from the boundaries of the reservoir.
Cause Sasha is the impact of external forces: changes in atmospheric pressure, wind, seismic phenomena.
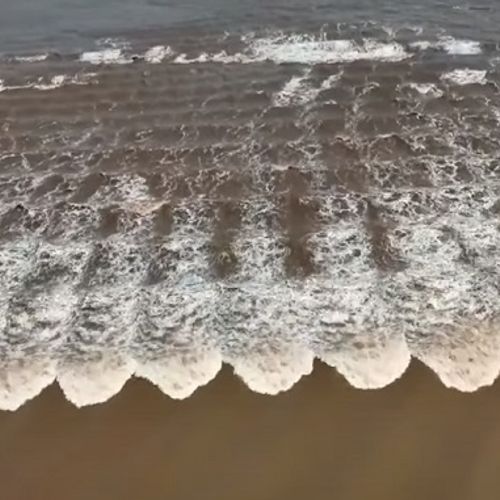
The duration of this phenomenon is quite large (from several minutes to tens of hours), and amplitude (from a few millimeters to several meters). Looks like a wave, as one or more bumps on the surface of the water in the same place with the same height and size.
Each normal oscillation appears to be a standing wave, unlike a traveling wave, standing still and has its own pattern of distribution of the amplitudes of the oscillations in space. It is possible to allocate antinodes – points where the oscillation amplitude reaches maxima, and nodes – stationary points where the amplitude is zero. At the same time, each wave oscillates with its own frequency.
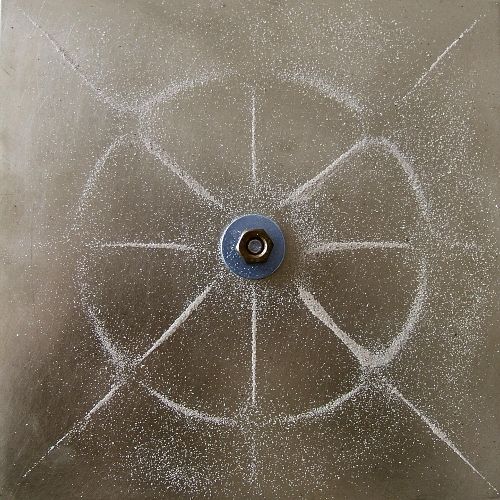
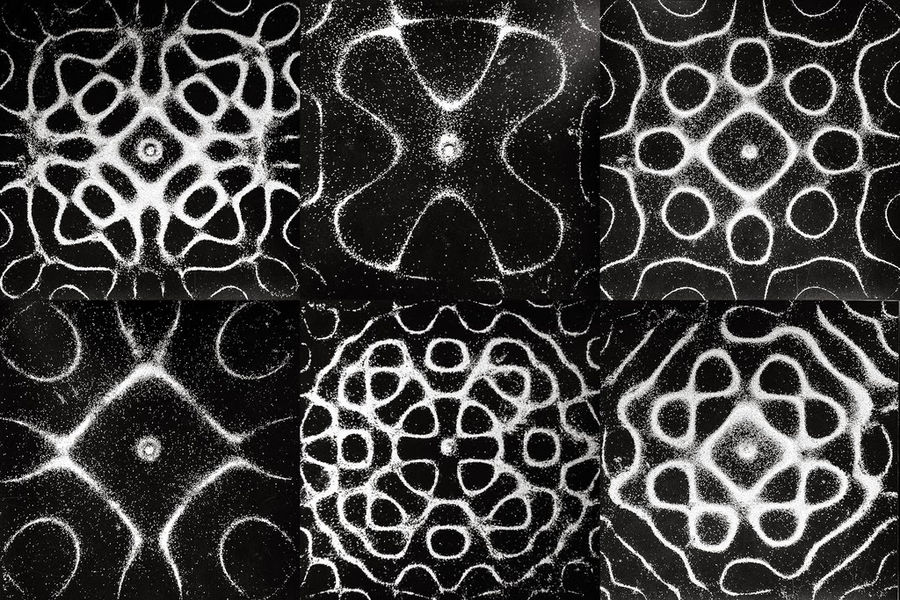
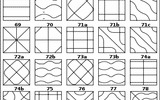
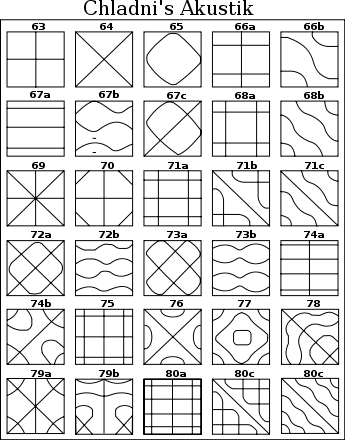
Chladni figures — the figures formed by the accumulation of small particles (e.g., sand) near loops or nodal lines on the surface of elastic oscillating plate.
Translated by «Yandex.Translator»
Related facts
Related news
Log in or register to post comments