| Added | Wed, 05/10/2016 |
| Hierarchy | |
| Область распространения | All over the world |
| Характерные признаки |
→
→
→
|
| Sources |
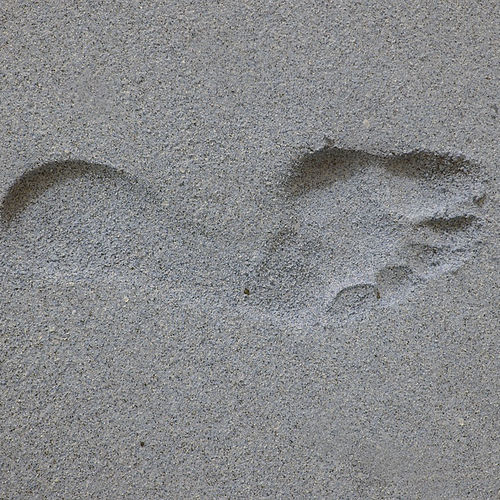
There are a huge number of different traces, which for various reasons are attributed to unexplained. We refer only hoof-like footprints to this phenomenon, since in all cases of their appearance there are common signs that differ from other phenomena in which the appearance of unusual footprints appears.
Hoof-like footprints in many cultures are traditionally associated with evil spirits. Different peoples consider devils, demons, the devil, as well as witches with hooves instead of legs, the damned, etc. to be the source of their origin.
Thus, the phenomenon of "devil's footprints" will be considered hoof-like signs that have appeared on various surfaces that have certain signs of deviation from the norm (the rate of occurrence, the distance between the prints, etc.)
The stories about the "devil's footprints" are rooted in remote antiquity. The very first mention can be considered the year 929. In Japan, "devilish traces" were observed on the territory of the imperial palace.
The earliest written mention that could be found dates back to 1205.
According to Ralph Cogeshell (who also described strange phenomena in his era), a writer of the 13th century, on July 19, 1205, strange hoof prints appeared after a severe thunderstorm.
The most famous case is considered to be an incident called "The Devil's Footprints in Devon", which may have taken place in February 1855 near the estuary of Aix in South Devon. A brief description of this fact: On the night of February 7-8, 1855, at 1.00 or 2.00, after a heavy snowfall, hoof-like signs appeared on the snow. These footprints, most of which measured about 4 inches long and about three inches wide, ranging from eight to sixteen inches apart and following approximately the same straight direction (albeit with slight deviations), were found in more than thirty locations throughout Devon and partly in Dorset. It was estimated that the total length of the route during which they met ranged from 40 to 100 miles. Houses, rivers, haystacks, fences and other obstacles did not stop the one who left these traces: they were found on the roofs of houses, their walls up to 14 feet high and even at the entrance and exit of small sewage pipes with a diameter of four inches. The tracks were so named because some people believed that they were the tracks of Satan, as they were allegedly made by cloven hooves. Many theories were put forward to explain this incident, and many aspects of it, as well as its reliability in general, were questioned even at that time; nevertheless, this event caused a rather serious (albeit short-term and quickly forgotten) mass hysteria.
There are very few primary sources telling about this event. Only documents found after the publication in 1950 of an article about the incident by the Devonshire Historical Society, which asked for help in finding additional information, are known. After that, a collection of articles and letters from the 1850s by Vicar Ellcombe was discovered, among which there is a letter to him from his friend Vicar Mcgrove, containing his letter to the newspaper The Illustrated London News marked "Not for print" and with a drawing of traces allegedly made from nature, and there were also found indications of other newspaper articles telling about this event; according to them, the identity of the first correspondent who told about the traces was established: he turned out to be the future curator of one of the Exter museums, who was 19 years old at that time.
There are four relatively reliable sources about the event, which are not far from him in time: letters from Ellacombe, a letter from Mcgrove, a report from Exeter and a certain letter from an anonymous author to one of the newspapers, in which he suggests that otters left the tracks. All subsequent articles, including those mentioned above, as well as Busk's 1890 article, where he cited eyewitness accounts, reprinted in 1922, appeared much later than the event, so they should be treated with caution.
There is information about several other similar incidents in other parts of the world, although none of them had the same scale as the case in Devon.
James Clark Ross wrote that during the Antarctic Expedition of 1839-1843 on the island of Kerguelen in 1840, he discovered strange horseshoe-shaped tracks - first on the ground, in the snow, and then on a rock where there was no snow. The tracks looked like the tracks of a horse or a donkey, but there were no such animals either on the expedition or on the island itself.
Fifteen years before the Devonian events, in 1840, The Times wrote that in Scotland, in Glen Orchy, on March 14, strange tracks similar to the prints of cloven hooves were found at a distance of up to 12 miles. The one who left them was, if we proceed from the depth of the tracks, a large size (about the size of a large foal) and at the same time limped.
In The Illustrated London News in March 1855, an article was published by a newspaper correspondent in Heidelberg, who, referring to an "authoritative Polish doctor of medicine," reported that on a Sandy Hill in the Kingdom of Poland, on the border with Galicia, such traces are found in the snow (and sometimes in the sand) every year, and local residents believe that they are being abandoned by a supernatural being.
1886: New Zealand.
1909: New Jersey, USA, beaches near Gloucester.
1945: Belgium.
1950: Devonshire (beach) again.
1952: Scotland.
1954: Brazil.
In the fall of 1957 in the magazine Tomorrow ("Tomorrow") An article by paranormal researcher Eric Dingwall titled "The Devil Walks Again" has appeared. It, in particular, cited the story of 26-year-old Colin Wilson (later a famous writer) about how in the summer of 1950, on one of the deserted sea beaches of Devonshire, he saw strange prints similar to hoofprints on the smooth and dense surface of wet sand, compacted by sea waves.
1974: The slopes of Etna, Sicily.
1976: Alps near Nice and near Lake Siljan (Norway).
Year 2000 (January 23): Cleveland (Ohio).
On March 12, 2009, there were reports in the press that the same traces appeared again at night in Devon, photos were even published, but official science did not give any comments on this.
This also includes various urban legends and stories about a woman with hooves. They do not have any specific geographical location. Very similar mentions of people with hooves are found almost throughout the territory of modern Russia and neighboring countries. Remotely similar urban legends are already known in almost all parts of the world.
For example, in the Voronezh Region, Verkhnyaya Khava and Kashirsky district are famous for the appearance of "women with hooves". At the same time, the cases and epics of the Upper Hava describe no longer the appearance of traces, but the "woman" herself. The case that occurred in the Kashirsky district in 1997 is rather similar to the Devonian one. Hypotheses of the origin of the "devil's footprints" are similar to hypotheses explaining the footprints from the incident in Devon.
Over the years, researcher Mike Dash, who collected materials about this event, summarized all the primary and secondary sources he found in the article "The Devil's Hoofmarks: Source Material on the Great Devon Mystery of 1855" ("Traces of the Devil: Materials for Studying the Great Devon Mystery of 1855"), first published in Fortean Studies in in 1994. He, without denying the reality of the fact as such, came to the conclusion that there was not and could not be any one "source" of the origin of the tracks: some of them were almost certainly a hoax, some were left by quite ordinary four-legged animals - for example, donkeys or horses, and some - mice. At the same time, he admitted that this could not explain all the reports of footprints (especially those allegedly found in cities), and that "the mystery remains."
Conventionally, they can be divided into mystical, natural and mystification.
A natural air balloon.
- Author Jeffrey Househall suggested that the traces were left by an experimental balloon, mistakenly released from Devonport, by means of links at the ends of its mooring ropes. The source of the version was a local resident, Major Carter, whose grandfather worked in Devonport at the time. Carter stated that the incident was hushed up because the balloon destroyed several winter gardens, greenhouses and windows before it landed on the ground in Honton. Although this version can explain the shape of the tracks, it seems very doubtful that the ball could follow such a strict trajectory for a long time and not catch the ropes on a tree or other object.
- Jumping mice. The aforementioned Mike Dash in his article indicates that at least some traces, especially those found on the roofs of houses, could well have been left by forest mice, which rushed to the cities due to unusually cold weather. The footprint that remains in the snow after the mouse jumps looks like a cloven hoof due to the movement of the mouse during the jump. Dash claims that the theory of the "mouse factor" appeared in The Illustrated London News back in March 1855 (because the article about this event, despite the request of the vicar, was still printed, for the first time - on February 13). It was noticed that in some places the tracks seemed to be interrupted after all, which was explained by the attack on mice by birds of prey (for example, owls), and allegedly the corpses of mice were even sometimes found next to the tracks. The mouse could also quite easily climb the walls and even crawl through the pipes. Thus, to date, the version about forest mice is the only one that could at least partially explain this event from the point of view of science.
- Mass hysteria. In addition, it was often assumed that this whole story was the result of a sudden mass hysteria caused by the comparison of various traces of the same origin (which could well have been left by cattle, badgers, otters, and so on) and their passing off as a single whole. This also includes the version of the origin of traces from known living beings.
- Kangaroo. In his letter to The Illustrated London News, Vicar Mcgrove wrote that there were rumors that a kangaroo had escaped from a private menagerie in Sidmouth. However, there are no sources of information on the reliability of this event, how a kangaroo could cross the estuary is unclear, and Mcgrove himself wrote then that he himself invented a story about a kangaroo to calm and distract his flock, who believed that the Devil really visited their land.
Mystical
- One-legged. According to one version, expressed by unknown people, the tracks were left by an animal called one-legged - he was reported to have been first seen in 1001 on the island of Labrador by a Viking Bjorf Heriolsen; the animal had only one leg, but moved with extraordinary speed. However, the newspaper that printed this version said that it was more likely to believe that the Devil really left the traces than to believe in the existence of a one-legged man.
- Jack the jumper. The history of the Devil's Footprints was also associated with Jack the Jumper, a character in the English urban legend of those times. But even if we assume that the Jack-jumper actually existed, then this version seems very doubtful. Firstly, Jack's appearances were not recorded in Devon at that time. Secondly, there is a description of the traces of the "real" Jack, and according to him they are not similar to those found in Devon. Jack the Jumper, or Spring-Heeled Jack (English Spring-Heeled Jack), is a character in English folklore of the Victorian era, a humanoid creature, notable primarily for its ability to make jumps of amazing height.
The very first reports of the appearance of Jack the Jumper in London are dated 1837. Later, his appearances were recorded in many places in England - especially in London itself, its suburbs, Liverpool, Sheffield, the Midlands (central England) and even Scotland. The "peak" of messages occurred in the 1850s-1880s; despite the fact that a number of reports of meetings with Jack from England and even other countries were received in the XX century, the last date of his appearance is considered to be 1904.
There are a large number of theories about the nature and personality of Jack the Jumper, but none of them is scientifically proven and does not give affirmative answers to all questions related to Jack's "activity". Thus, his story remains unexplained to this day, science does not know about the device with which a person could make Jack-like jumps, and the fact of his real existence is disputed by a significant number of historians. The urban legend of Jack the Jumper was incredibly popular in England in the second half of the XIX century - primarily because of his unusual appearance, aggressive eccentric behavior (Jack often attacked people) and the mentioned ability to make incredible jumps in height, to the point that Jack became the hero of several works of fiction."tabloid literature" of the XIX-XX centuries.
The story of Jack the Jumper is significant because of two points. Firstly, his image had a huge impact on the "comic culture" of the XX century, and it was his attire that became the prototype of the "superhero (or supervillain) costume". Secondly, it is the only "intelligent mystical being" in the history of mankind, whose "case" was discussed at the level of a state institution that came to recognize its reality.
There are many versions of hoax methods.
- For example, that the traces could have been left by some "unknown hot metal object".
Phenomenon in mass culture
Phenomena
Related versions
Related facts
Related news
Related articles
Log in or register to post comments